pyvista.ExplicitStructuredGrid#
- class ExplicitStructuredGrid(*args, deep: bool = False, **kwargs)[source]#
Extend the functionality of the
vtk.vtkExplicitStructuredGridclass.Can be initialized by the following:
Creating an empty grid
From a
vtk.vtkExplicitStructuredGridorvtk.vtkUnstructuredGridobjectFrom a VTU or VTK file
From
dimsandcornersarrays
- Parameters:
Examples
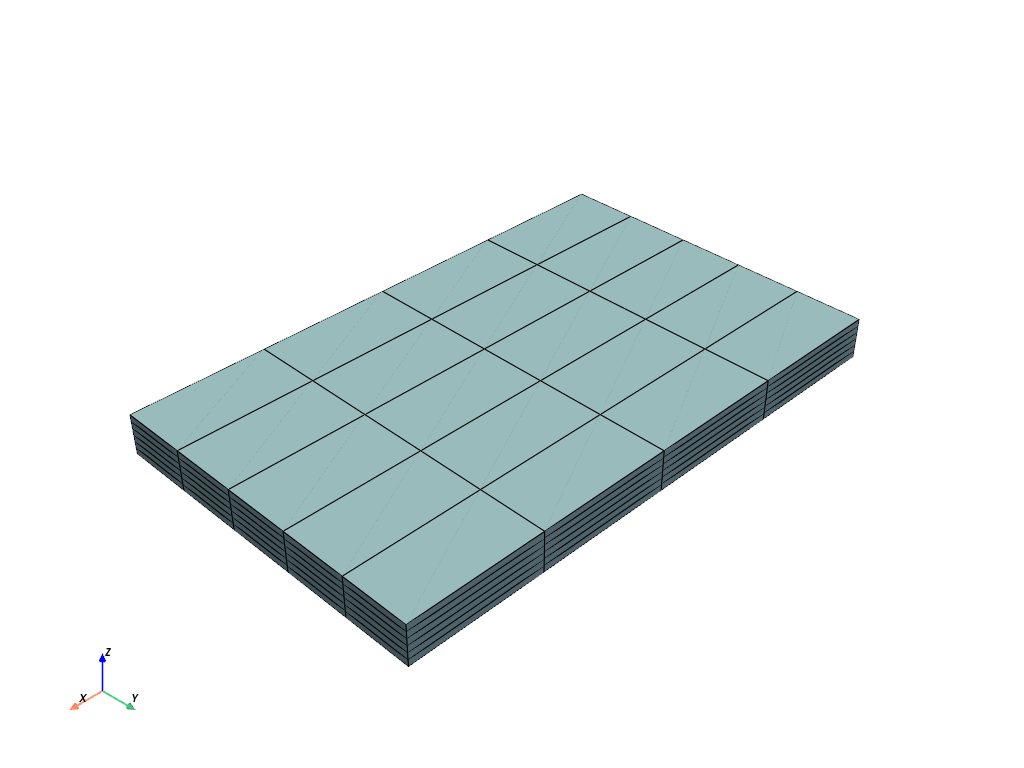
>>> import numpy as np >>> import pyvista as pv >>> >>> # grid size: ni*nj*nk cells; si, sj, sk steps >>> ni, nj, nk = 4, 5, 6 >>> si, sj, sk = 20, 10, 1 >>> >>> # create raw coordinate grid >>> grid_ijk = np.mgrid[ ... : (ni + 1) * si : si, ... : (nj + 1) * sj : sj, ... : (nk + 1) * sk : sk, ... ] >>> >>> # repeat array along each Cartesian axis for connectivity >>> for axis in range(1, 4): ... grid_ijk = grid_ijk.repeat(2, axis=axis) ... >>> >>> # slice off unnecessarily doubled edge coordinates >>> grid_ijk = grid_ijk[:, 1:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1] >>> >>> # reorder and reshape to VTK order >>> corners = grid_ijk.transpose().reshape(-1, 3) >>> >>> dims = np.array([ni, nj, nk]) + 1 >>> grid = pv.ExplicitStructuredGrid(dims, corners) >>> grid = grid.compute_connectivity() >>> grid.plot(show_edges=True)
Methods
Cast to an unstructured grid.
Return the cell structured coordinates.
ExplicitStructuredGrid.cell_id(coords)Return the cell ID.
Compute an array with the number of connected cell faces.
Compute the faces connectivity flags array.
ExplicitStructuredGrid.hide_cells(ind[, inplace])Hide specific cells.
ExplicitStructuredGrid.neighbors(ind[, rel])Return the indices of neighboring cells.
ExplicitStructuredGrid.save(filename[, ...])Save this VTK object to file.
ExplicitStructuredGrid.show_cells([inplace])Show hidden cells.
Attributes
Return the topological dimensions of the grid.
Return the bounding box of the visible cells.