Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Visualize the Moeller–Trumbore Algorithm#
This example demonstrates the Moeller–Trumbore intersection algorithm using pyvista.
For additional details, please reference the following:
First, define the ray triangle intersection method.
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
def ray_triangle_intersection(ray_start, ray_vec, triangle):
"""Moeller–Trumbore intersection algorithm.
Parameters
----------
ray_start : np.ndarray
Length three numpy array representing start of point.
ray_vec : np.ndarray
Direction of the ray.
triangle : np.ndarray
``3 x 3`` numpy array containing the three vertices of a
triangle.
Returns
-------
bool
``True`` when there is an intersection.
tuple
Length three tuple containing the distance ``t``, and the
intersection in unit triangle ``u``, ``v`` coordinates. When
there is no intersection, these values will be:
``[np.nan, np.nan, np.nan]``
"""
# define a null intersection
null_inter = np.array([np.nan, np.nan, np.nan])
# break down triangle into the individual points
v1, v2, v3 = triangle
eps = 0.000001
# compute edges
edge1 = v2 - v1
edge2 = v3 - v1
pvec = np.cross(ray_vec, edge2)
det = edge1.dot(pvec)
if abs(det) < eps: # no intersection
return False, null_inter
inv_det = 1.0 / det
tvec = ray_start - v1
u = tvec.dot(pvec) * inv_det
if u < 0.0 or u > 1.0: # if not intersection
return False, null_inter
qvec = np.cross(tvec, edge1)
v = ray_vec.dot(qvec) * inv_det
if v < 0.0 or u + v > 1.0: # if not intersection
return False, null_inter
t = edge2.dot(qvec) * inv_det
if t < eps:
return False, null_inter
return True, np.array([t, u, v])
# Create a basic triangle within pyvista
points = np.array([[0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0]])
faces = np.array([3, 0, 1, 2])
tri = pv.PolyData(points, faces)
# cast a ray above pointed downwards
start = np.array([0.3, 0.25, 1])
direction = np.array([0, 0, -1])
# compute if the intersection exists
inter, tuv = ray_triangle_intersection(start, direction, points)
t, u, v = tuv
print('Intersected', inter)
print('t:', t)
print('u:', u)
print('v:', v)
/home/runner/work/pyvista/pyvista/pyvista/core/utilities/points.py:52: UserWarning: Points is not a float type. This can cause issues when transforming or applying filters. Casting to ``np.float32``. Disable this by passing ``force_float=False``.
warnings.warn(
Intersected True
t: 1.0
u: 0.25
v: 0.3
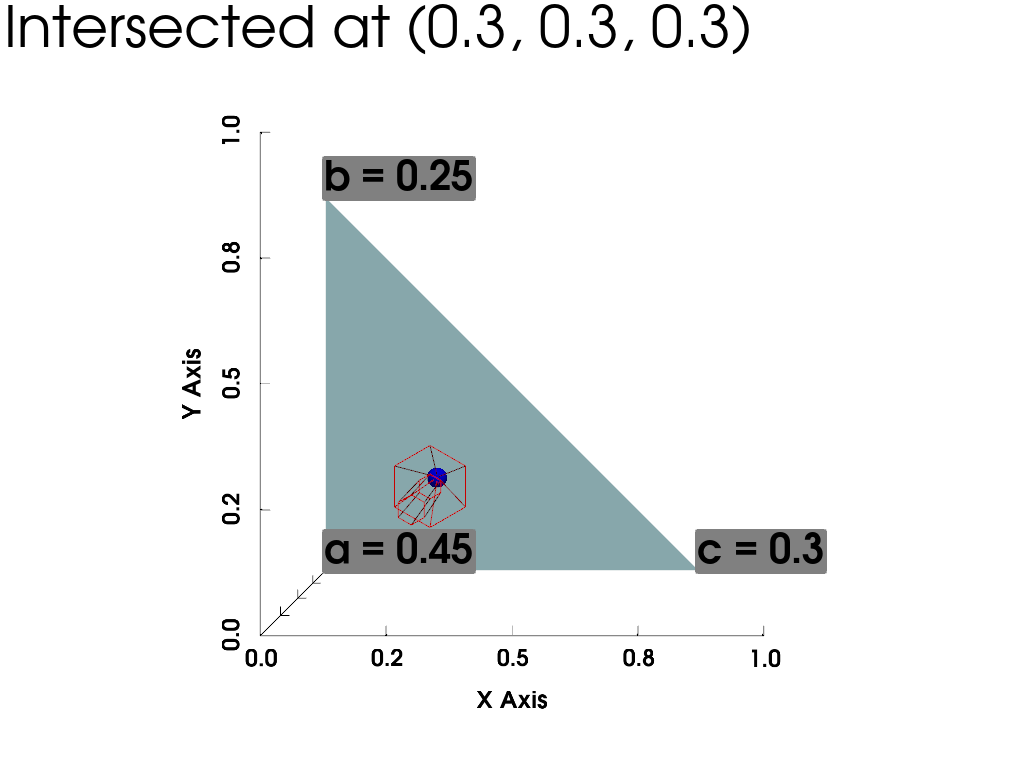
Plot the problem setup and the intersection
if inter:
# reconstruct intersection point in barycentric coordinates. See
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barycentric_coordinate_system
a, b, c = (1 - u - v), u, v
point = tri.points[0] * a + tri.points[1] * b + tri.points[2] * c
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_text(f'Intersected at ({point[0]:.3}, {point[0]:.3}, {point[0]:.3})', font_size=26)
pl.add_mesh(tri)
_ = pl.add_arrows(
np.array([start]),
np.array([direction]),
show_scalar_bar=False,
color='r',
style='wireframe',
)
pl.add_points(np.array([point]), point_size=20, render_points_as_spheres=True, color='b')
pl.add_point_labels(tri, [f'a = {1 - u - v:.3}', f'b = {u:.3}', f'c = {v:.3}'], font_size=40)
pl.show_bounds()
pl.camera_position = 'xy'
pl.show()
else: # no intersection
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_text('No intersection')
_ = pl.add_arrows(
np.array([start]),
np.array([direction]),
show_scalar_bar=False,
color='r',
style='wireframe',
)
pl.add_mesh(tri)
pl.show_bounds()
pl.camera_position = 'xy'
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.341 seconds)