Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Create Triangulated Surface#
Create a surface from a set of points through a Delaunay triangulation.
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
Simple Triangulations#
First, create some points for the surface.
# Define a simple Gaussian surface
n = 20
x = np.linspace(-200, 200, num=n) + np.random.uniform(-5, 5, size=n)
y = np.linspace(-200, 200, num=n) + np.random.uniform(-5, 5, size=n)
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y)
A, b = 100, 100
zz = A * np.exp(-0.5 * ((xx / b) ** 2.0 + (yy / b) ** 2.0))
# Get the points as a 2D NumPy array (N by 3)
points = np.c_[xx.reshape(-1), yy.reshape(-1), zz.reshape(-1)]
points[0:5, :]
array([[-203.29298421, -197.18803352, 1.81232814],
[-183.19143671, -197.18803352, 2.67261938],
[-159.80476405, -197.18803352, 3.99137597],
[-133.86679653, -197.18803352, 5.84156183],
[-118.69668914, -197.18803352, 7.07501071]])
Now use those points to create a point cloud PyVista data object. This will
be encompassed in a pyvista.PolyData object.
# simply pass the numpy points to the PolyData constructor
cloud = pv.PolyData(points)
cloud.plot(point_size=15)
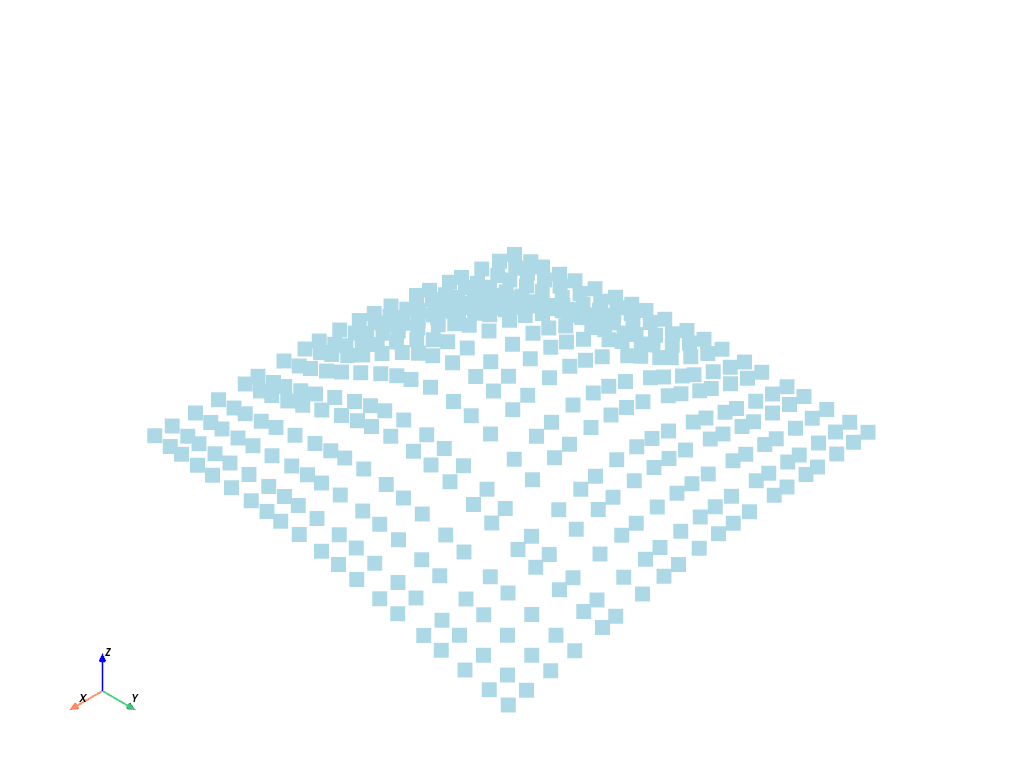
Now that we have a PyVista data structure of the points, we can perform a triangulation to turn those boring discrete points into a connected surface.
surf = cloud.delaunay_2d()
surf.plot(show_edges=True)
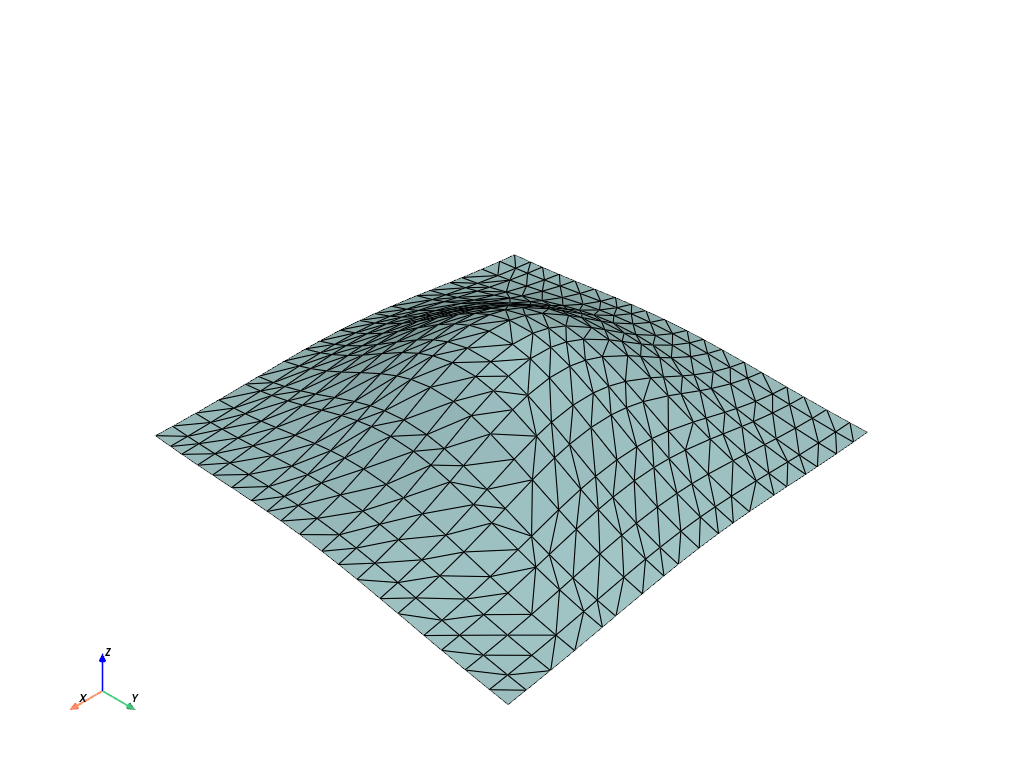
Masked Triangulations#
x = np.arange(10, dtype=float)
xx, yy, zz = np.meshgrid(x, x, [0])
points = np.column_stack((xx.ravel(order="F"), yy.ravel(order="F"), zz.ravel(order="F")))
# Perturb the points
points[:, 0] += np.random.rand(len(points)) * 0.3
points[:, 1] += np.random.rand(len(points)) * 0.3
# Create the point cloud mesh to triangulate from the coordinates
cloud = pv.PolyData(points)
cloud
Run the triangulation on these points
surf = cloud.delaunay_2d()
surf.plot(cpos="xy", show_edges=True)
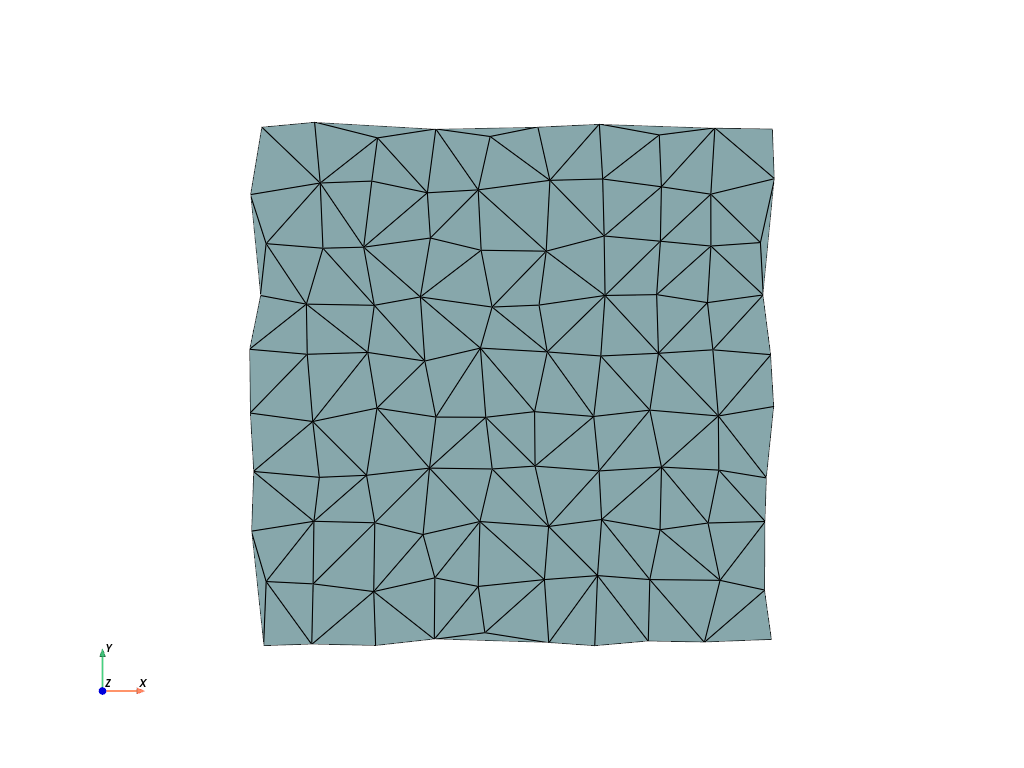
Note that some of the outer edges are unconstrained and the triangulation
added unwanted triangles. We can mitigate that with the alpha parameter.
surf = cloud.delaunay_2d(alpha=1.0)
surf.plot(cpos="xy", show_edges=True)
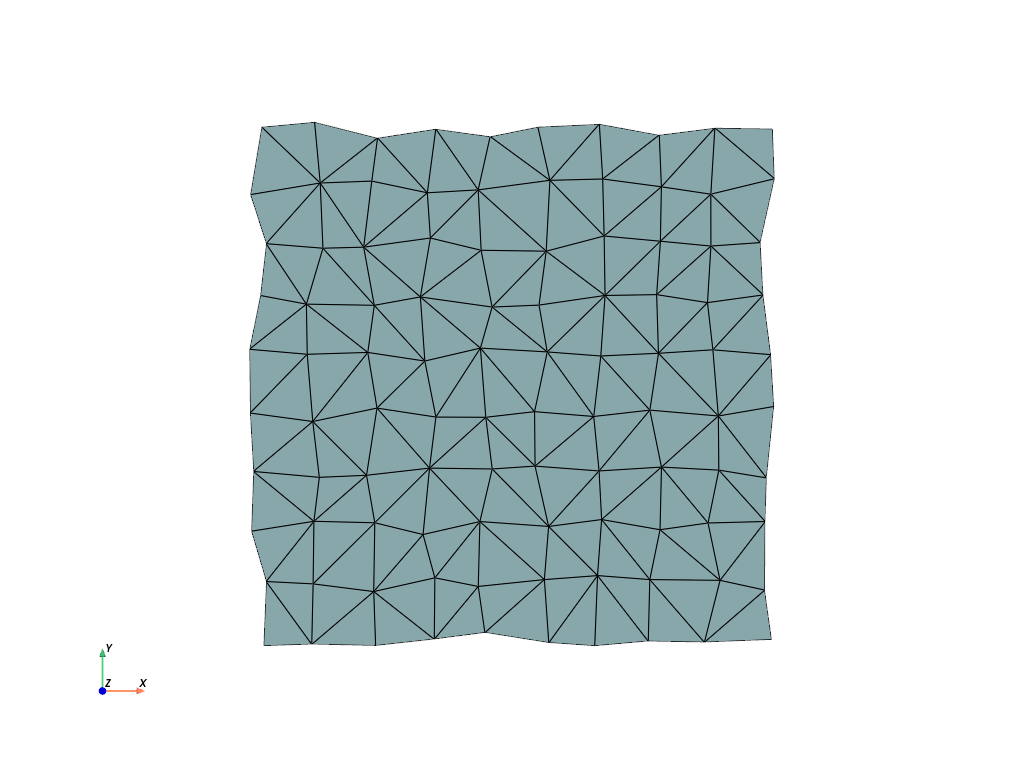
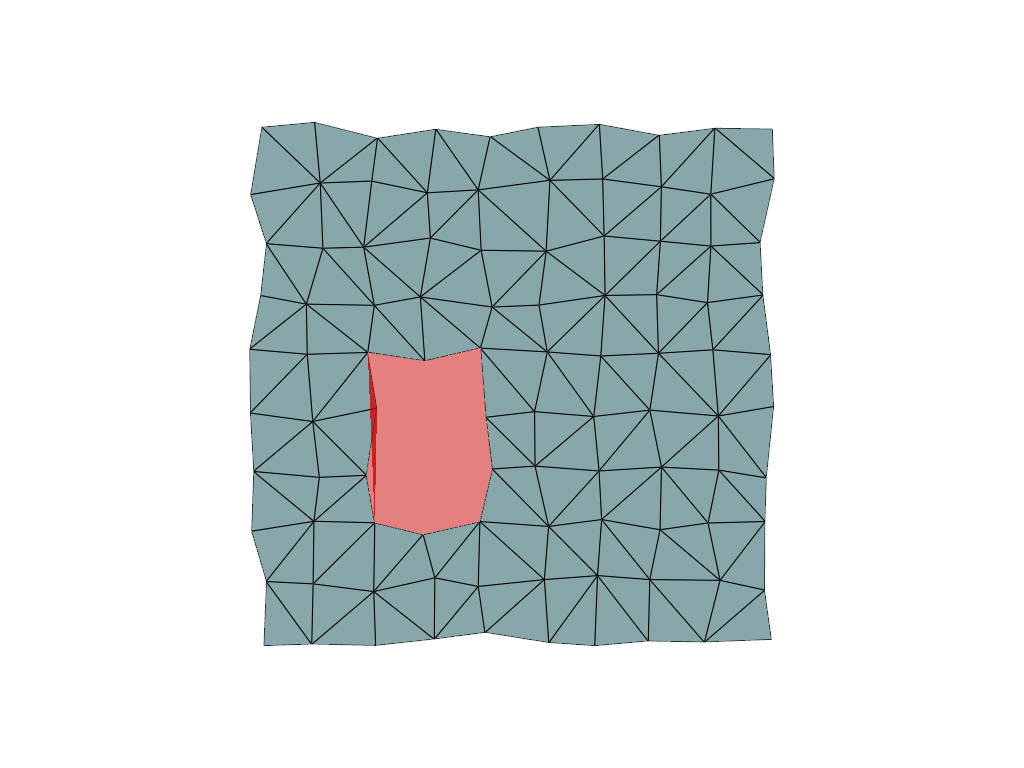
We could also add a polygon to ignore during the triangulation via the
edge_source parameter.
# Define a polygonal hole with a clockwise polygon
ids = [22, 23, 24, 25, 35, 45, 44, 43, 42, 32]
# Create a polydata to store the boundary
polygon = pv.PolyData()
# Make sure it has the same points as the mesh being triangulated
polygon.points = points
# But only has faces in regions to ignore
polygon.faces = np.insert(ids, 0, len(ids))
surf = cloud.delaunay_2d(alpha=1.0, edge_source=polygon)
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(surf, show_edges=True)
p.add_mesh(polygon, color="red", opacity=0.5)
p.show(cpos="xy")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.024 seconds)