pyvista.DataSetFilters.interpolate#
- DataSetFilters.interpolate(target, sharpness=2.0, radius=1.0, strategy='null_value', null_value=0.0, n_points=None, pass_cell_data=True, pass_point_data=True, progress_bar=False)[source]#
Interpolate values onto this mesh from a given dataset.
The
targetdataset is typically a point cloud. Only point data from thetargetmesh will be interpolated onto points of this mesh. Whether preexisting point and cell data of this mesh are preserved in the output can be customized with thepass_point_dataandpass_cell_dataparameters.This uses a Gaussian interpolation kernel. Use the
sharpnessandradiusparameters to adjust this kernel. You can also switch this kernel to use an N closest points approach.If the cell topology is more useful for interpolating, e.g. from a discretized FEM or CFD simulation, use
pyvista.DataSetFilters.sample()instead.- Parameters:
- target
pyvista.DataSet The vtk data object to sample from. Point and cell arrays from this object are interpolated onto this mesh.
- sharpness
float, default: 2.0 Set the sharpness (i.e., falloff) of the Gaussian kernel. As the sharpness increases the effects of distant points are reduced.
- radius
float,optional Specify the radius within which the basis points must lie.
- strategy
str, default: “null_value” Specify a strategy to use when encountering a “null” point during the interpolation process. Null points occur when the local neighborhood (of nearby points to interpolate from) is empty. If the strategy is set to
'mask_points', then an output array is created that marks points as being valid (=1) or null (invalid =0) (and the NullValue is set as well). If the strategy is set to'null_value', then the output data value(s) are set to thenull_value(specified in the output point data). Finally, the strategy'closest_point'is to simply use the closest point to perform the interpolation.- null_value
float, default: 0.0 Specify the null point value. When a null point is encountered then all components of each null tuple are set to this value.
- n_points
int,optional If given, specifies the number of the closest points used to form the interpolation basis. This will invalidate the radius argument in favor of an N closest points approach. This typically has poorer results.
- pass_cell_databool, default:
True Preserve input mesh’s original cell data arrays.
- pass_point_databool, default:
True Preserve input mesh’s original point data arrays.
- progress_barbool, default:
False Display a progress bar to indicate progress.
- target
- Returns:
pyvista.DataSetInterpolated dataset. Return type matches input.
See also
Examples
Interpolate the values of 5 points onto a sample plane.
>>> import pyvista as pv >>> import numpy as np >>> np.random.seed(7) >>> point_cloud = np.random.random((5, 3)) >>> point_cloud[:, 2] = 0 >>> point_cloud -= point_cloud.mean(0) >>> pdata = pv.PolyData(point_cloud) >>> pdata['values'] = np.random.random(5) >>> plane = pv.Plane() >>> plane.clear_data() >>> plane = plane.interpolate(pdata, sharpness=3) >>> pl = pv.Plotter() >>> _ = pl.add_mesh( ... pdata, render_points_as_spheres=True, point_size=50 ... ) >>> _ = pl.add_mesh(plane, style='wireframe', line_width=5) >>> pl.show()
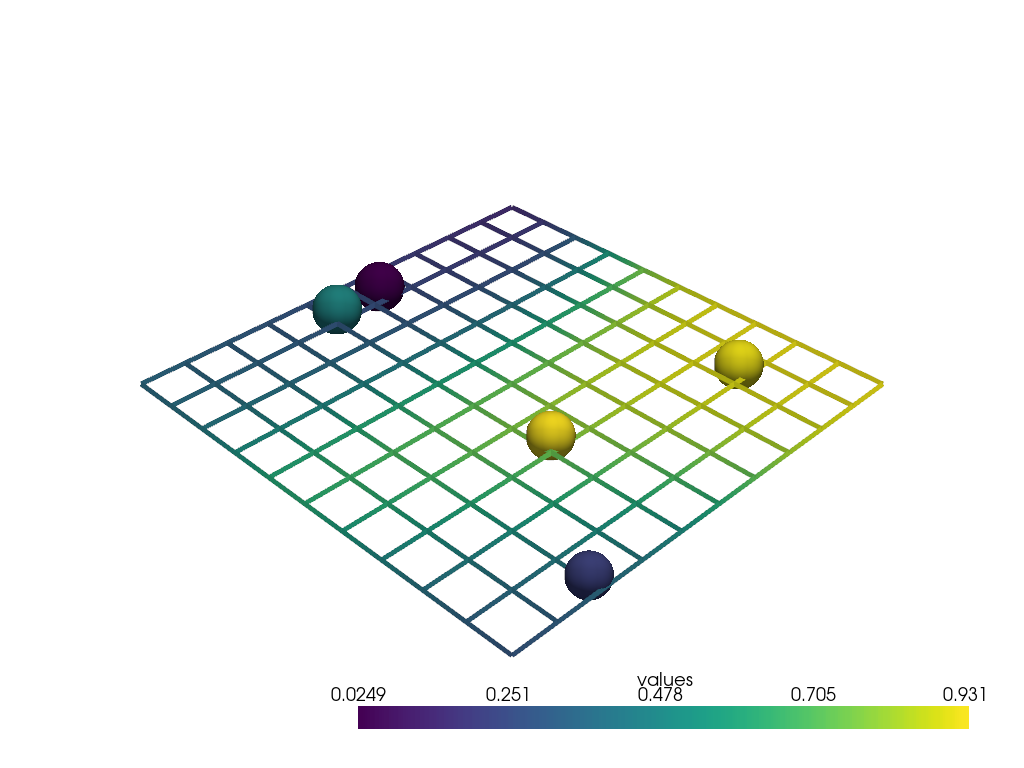
See Interpolating for more examples using this filter.