Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Plotting Glyphs (Vectors or PolyData)#
Use vectors in a dataset to plot and orient glyphs/geometric objects.
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
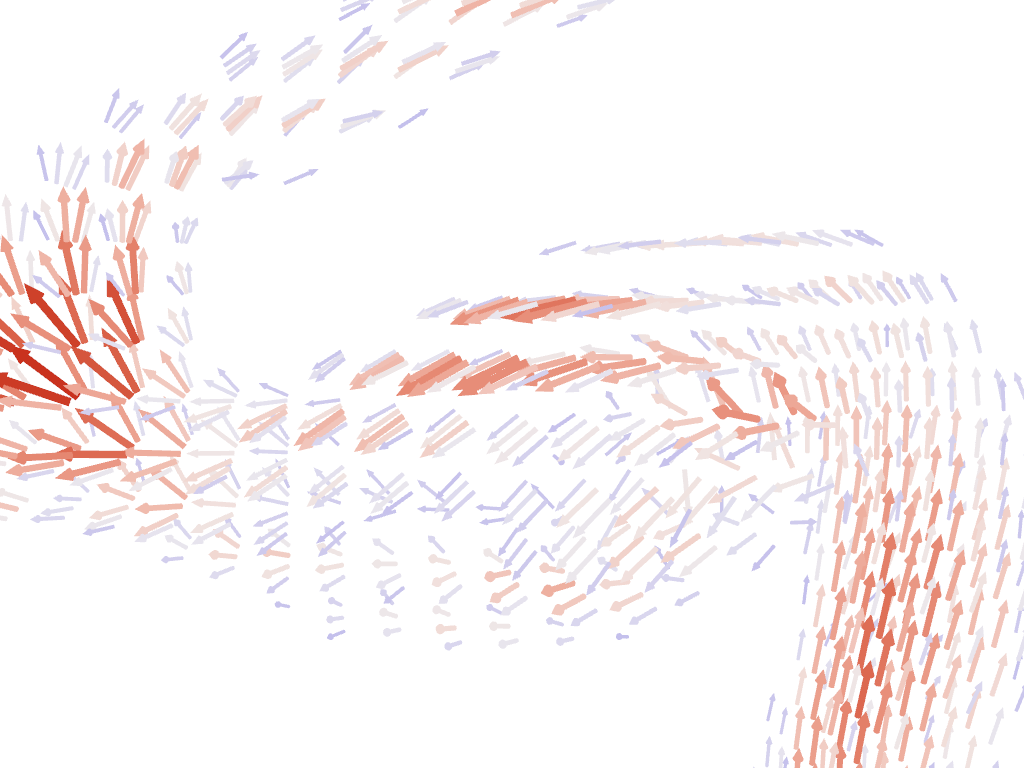
Glyphying can be done via the pyvista.DataSetFilters.glyph() filter
mesh = examples.download_carotid().threshold(145, scalars="scalars")
mask = mesh['scalars'] < 210
mesh['scalars'][mask] = 0 # null out smaller vectors
# Make a geometric object to use as the glyph
geom = pv.Arrow() # This could be any dataset
# Perform the glyph
glyphs = mesh.glyph(orient="vectors", scale="scalars", factor=0.003, geom=geom)
# plot using the plotting class
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(glyphs, show_scalar_bar=False, lighting=False, cmap='coolwarm')
pl.camera_position = [
(146.53, 91.28, 21.70),
(125.00, 94.45, 19.81),
(-0.086, 0.007, 0.996),
] # view only part of the vector field
cpos = pl.show(return_cpos=True)
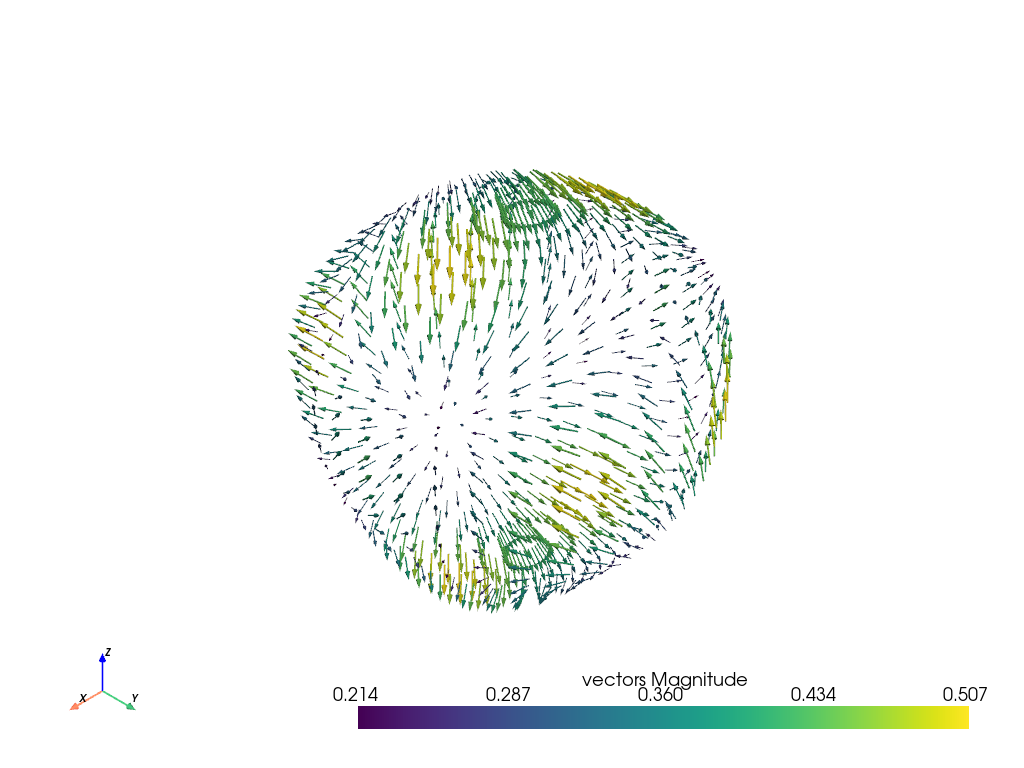
Another approach is to load the vectors directly to the mesh object and then
access the pyvista.DataSet.arrows property.
sphere = pv.Sphere(radius=3.14)
# make cool swirly pattern
vectors = np.vstack(
(
np.sin(sphere.points[:, 0]),
np.cos(sphere.points[:, 1]),
np.cos(sphere.points[:, 2]),
)
).T
# add and scale
sphere["vectors"] = vectors * 0.3
sphere.set_active_vectors("vectors")
# plot just the arrows
sphere.arrows.plot()
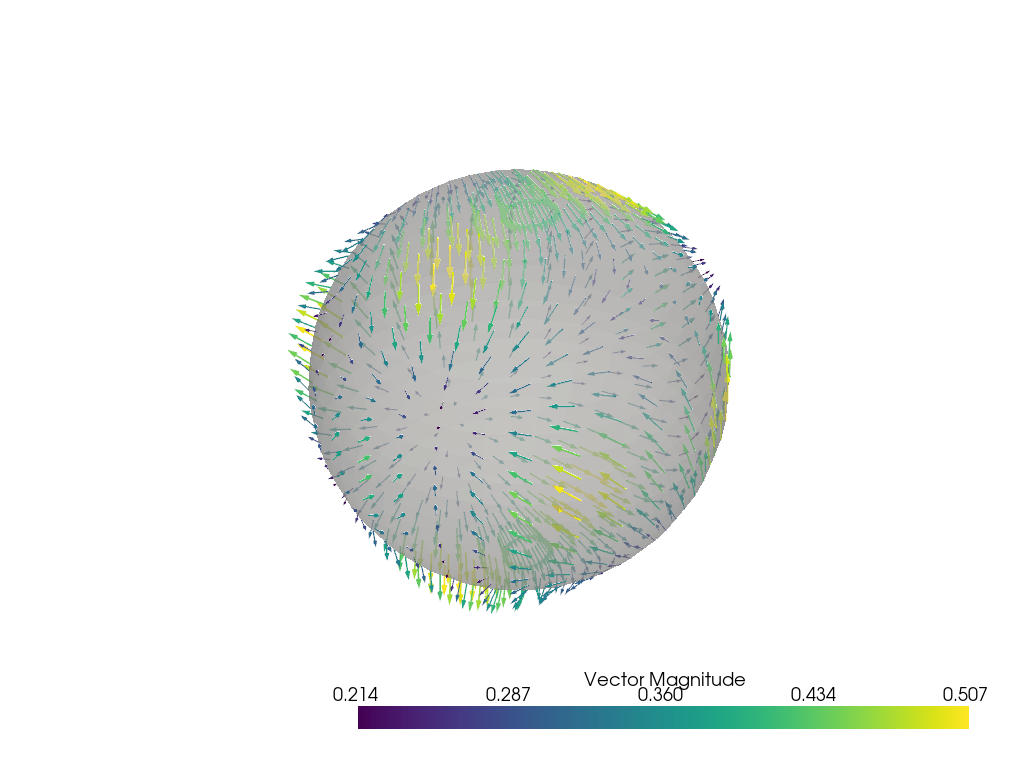
Plot the arrows and the sphere.
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(sphere.arrows, lighting=False, scalar_bar_args={'title': "Vector Magnitude"})
p.add_mesh(sphere, color="grey", ambient=0.6, opacity=0.5, show_edges=False)
p.show()
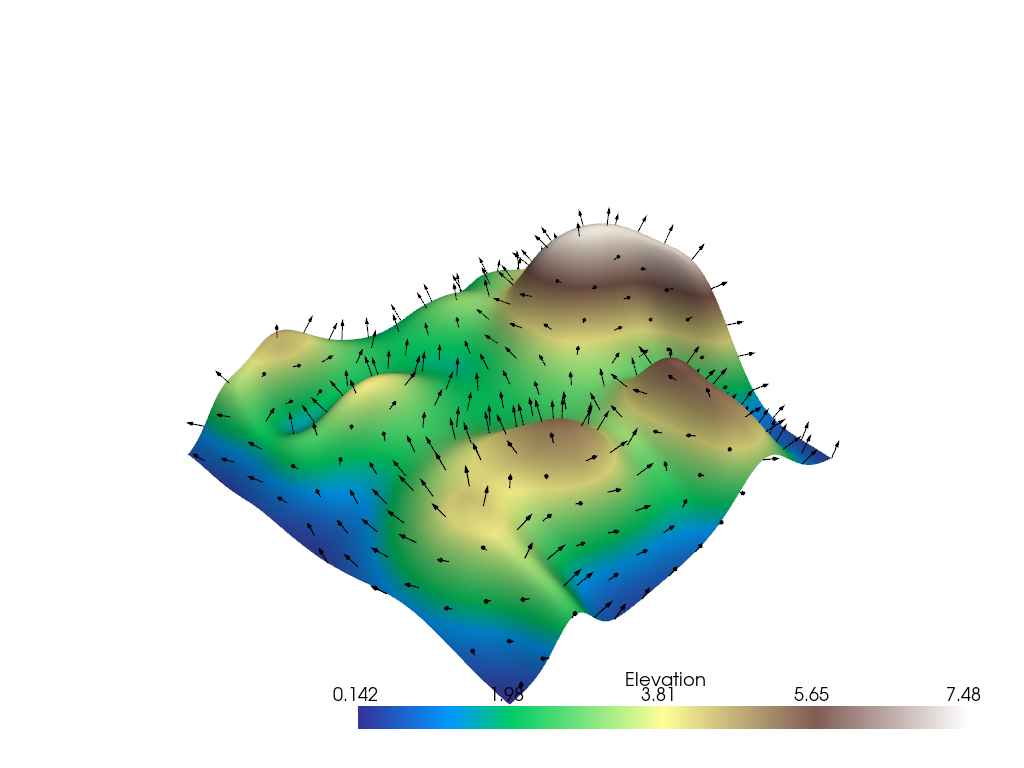
Subset of Glyphs#
Sometimes you might not want glyphs for every node in the input dataset. In this case, you can choose to build glyphs for a subset of the input dataset by using a merging tolerance. Here we specify a merging tolerance of five percent which equates to five percent of the bounding box’s length.
# Example dataset with normals
mesh = examples.load_random_hills()
# create a subset of arrows using the glyph filter
arrows = mesh.glyph(scale="Normals", orient="Normals", tolerance=0.05)
p = pv.Plotter()
p.add_mesh(arrows, color="black")
p.add_mesh(mesh, scalars="Elevation", cmap="terrain", smooth_shading=True)
p.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 12.639 seconds)