Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Gaussian Smoothing#
Perform a Gaussian convolution on a uniformly gridded data set.
pyvista.ImageData data sets (a.k.a. images) a can be smoothed by
convolving the image data set with a Gaussian for one- to three-dimensional
inputs. This is commonly referred to as Gaussian blurring and typically used
to reduce noise or decrease the detail of an image dataset.
See also pyvista.ImageDataFilters.gaussian_smooth().
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
# Load dataset
data = examples.download_gourds()
# Define a good point of view
cp = [(319.5, 239.5, 1053.7372980874645), (319.5, 239.5, 0.0), (0.0, 1.0, 0.0)]
Let’s apply the Gaussian smoothing with different values of standard deviation.
p = pv.Plotter(shape=(2, 2))
p.subplot(0, 0)
p.add_text("Original Image", font_size=14)
p.add_mesh(data, rgb=True)
p.camera_position = cp
p.subplot(0, 1)
p.add_text("Gaussian smoothing, std=2", font_size=14)
p.add_mesh(data.gaussian_smooth(std_dev=2.0), rgb=True)
p.camera_position = cp
p.subplot(1, 0)
p.add_text("Gaussian smoothing, std=4", font_size=14)
p.add_mesh(data.gaussian_smooth(std_dev=4.0), rgb=True)
p.camera_position = cp
p.subplot(1, 1)
p.add_text("Gaussian smoothing, std=8", font_size=14)
p.add_mesh(data.gaussian_smooth(std_dev=8.0), rgb=True)
p.camera_position = cp
p.show()

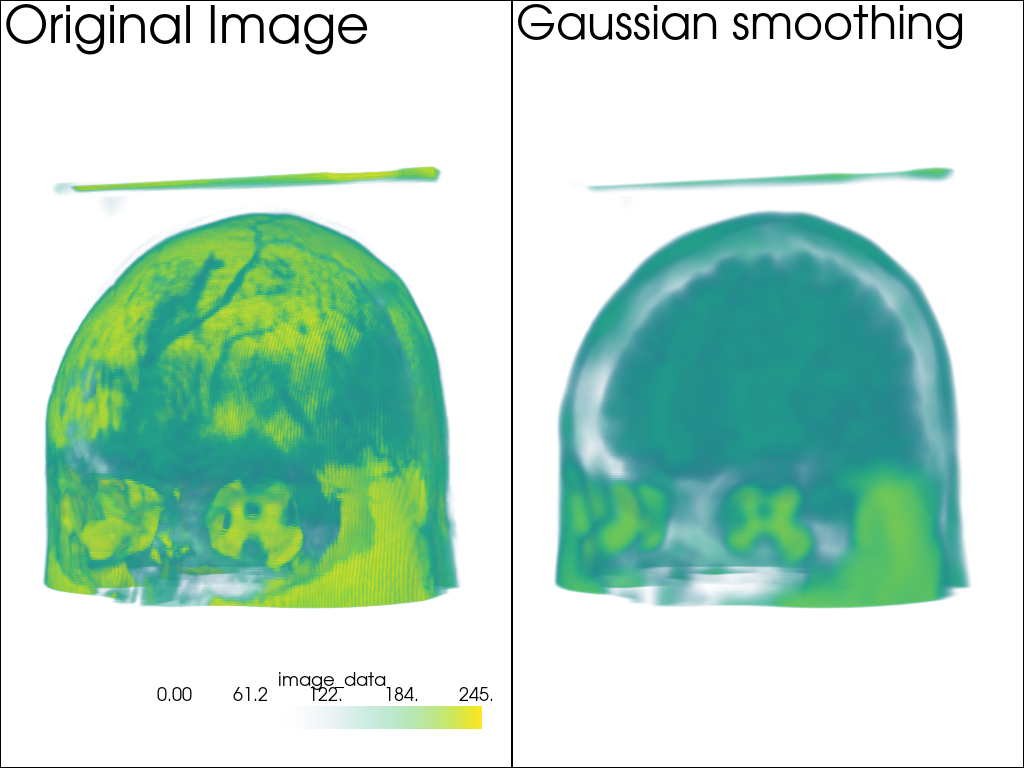
Volume Rendering#
Now let’s see an example on a 3D dataset with volume rendering:
data = examples.download_brain()
smoothed_data = data.gaussian_smooth(std_dev=3.0)
dargs = dict(clim=smoothed_data.get_data_range(), opacity=[0, 0, 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1])
n = [100, 150, 200, 245, 255]
p = pv.Plotter(shape=(1, 2))
p.subplot(0, 0)
p.add_text("Original Image", font_size=24)
# p.add_mesh(data.contour(n), **dargs)
p.add_volume(data, **dargs)
p.subplot(0, 1)
p.add_text("Gaussian smoothing", font_size=24)
# p.add_mesh(smoothed_data.contour(n), **dargs)
p.add_volume(smoothed_data, **dargs)
p.link_views()
p.camera_position = [(-162.0, 704.8, 65.02), (90.0, 108.0, 90.0), (0.0068, 0.0447, 0.999)]
p.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 14.750 seconds)