Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Surface Smoothing#
Smoothing rough edges of a surface mesh
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
Suppose you extract a volumetric subset of a dataset that has roughly defined
edges. Perhaps you’d like a smooth representation of that model region. This
can be achieved by extracting the bounding surface of the volume and applying
a pyvista.PolyDataFilters.smooth() filter.
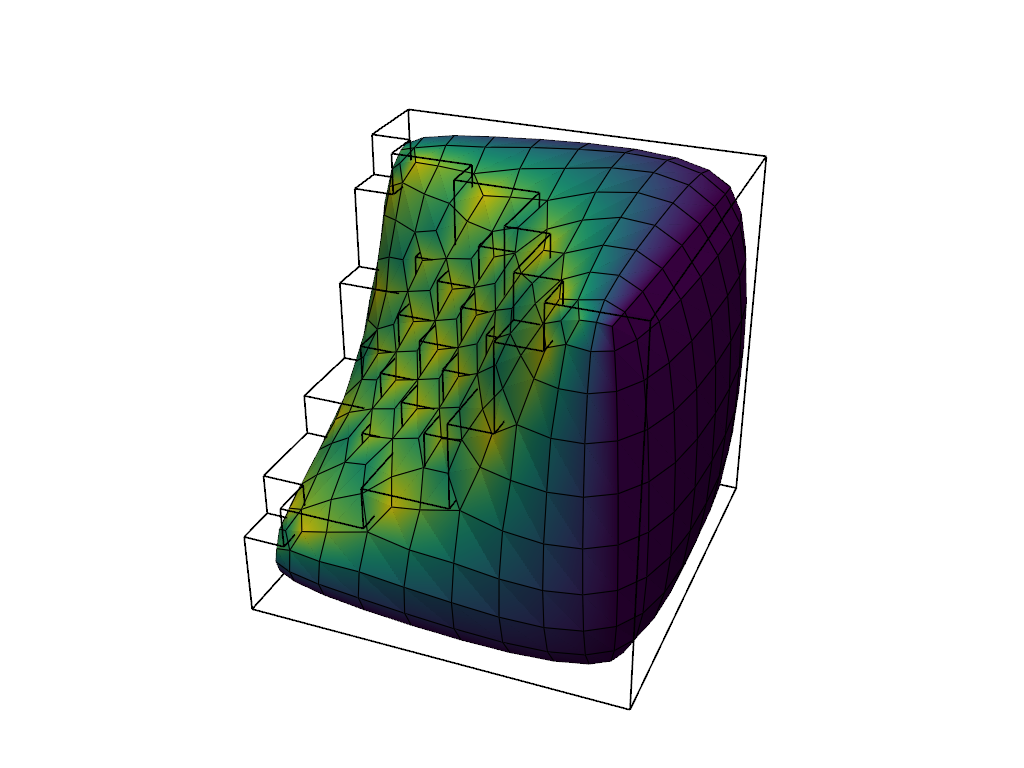
The below code snippet loads a sample roughly edged volumetric dataset:
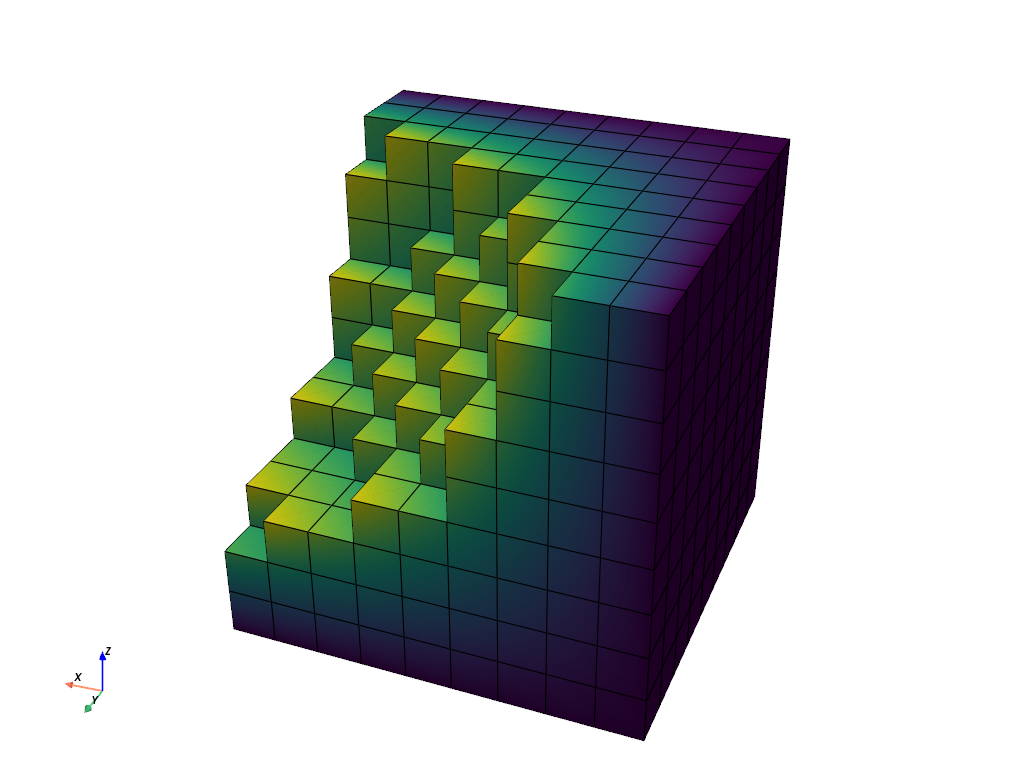
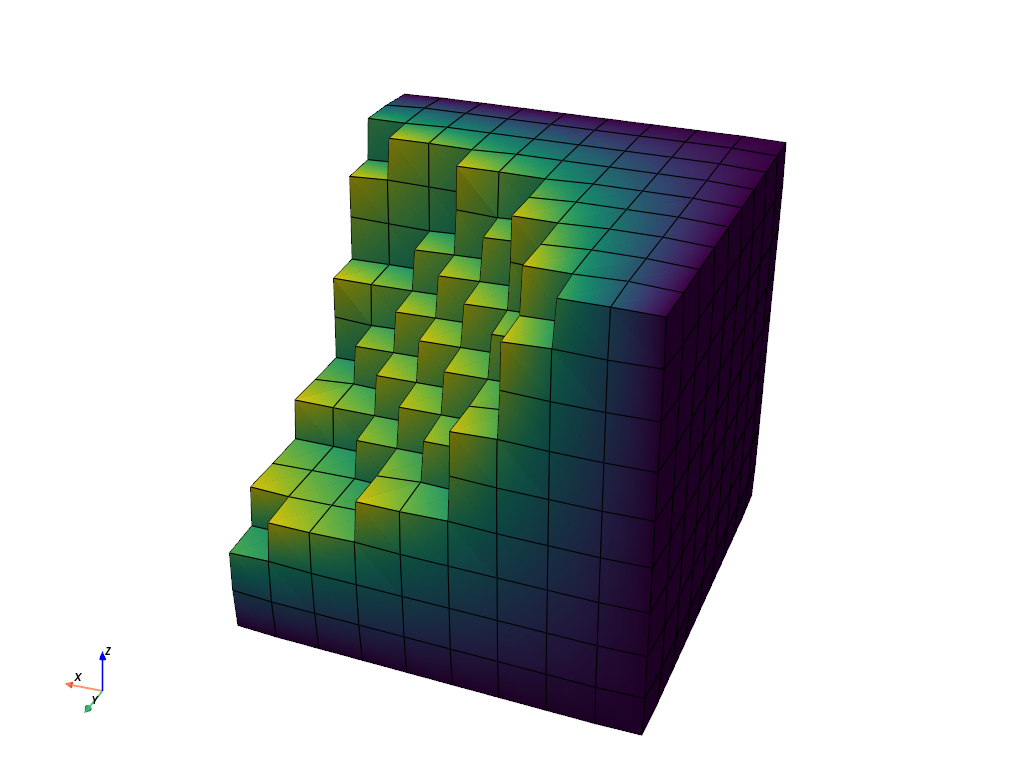
Extract the outer surface of the volume using the
pyvista.DataSetFilters.extract_geometry() filter and then apply the
smoothing filter:
Not smooth enough? Try increasing the number of iterations for the Laplacian smoothing algorithm:
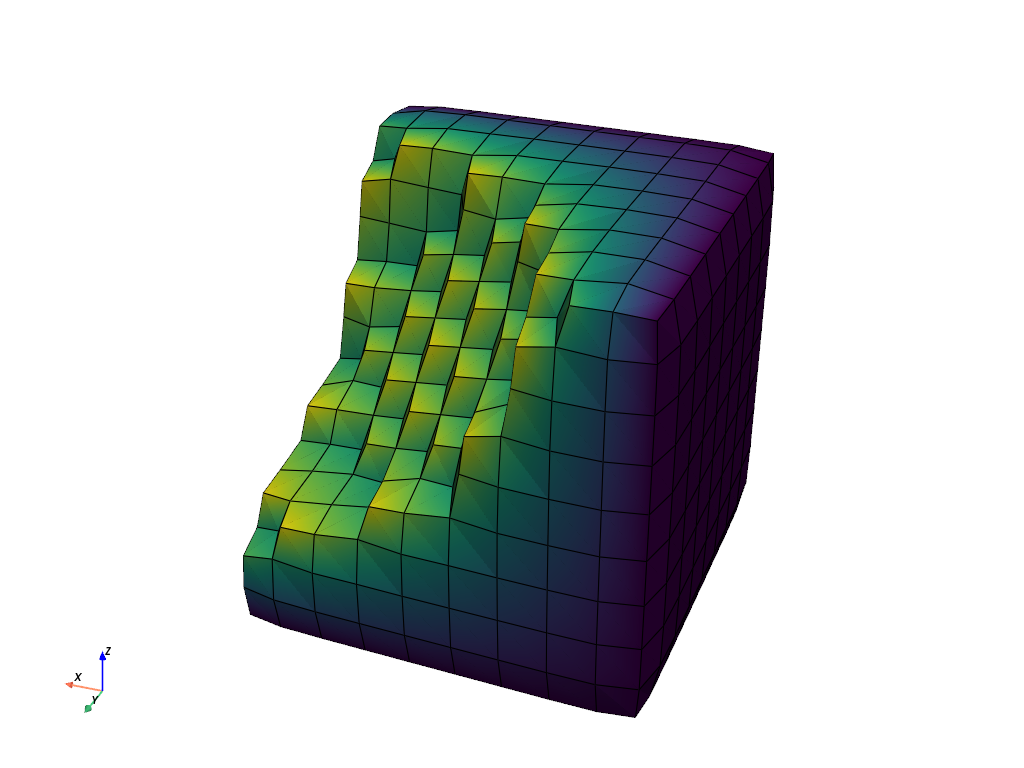
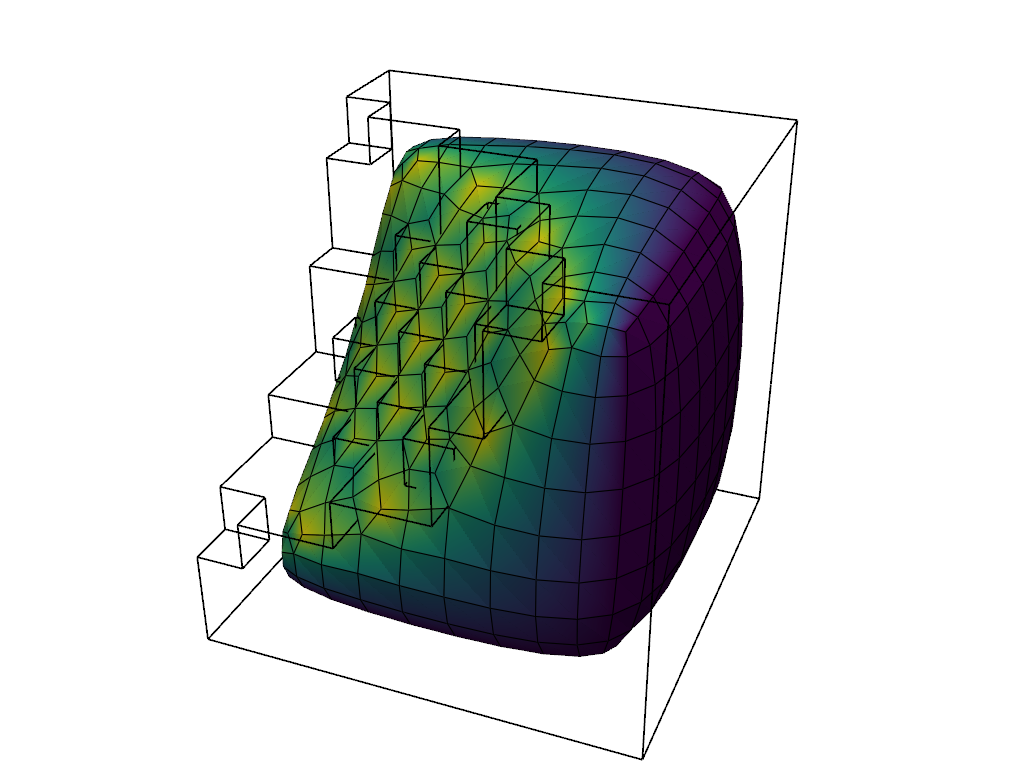
Still not smooth enough? Increase the number of iterations for the Laplacian smoothing algorithm to a crazy high value. Note how this causes the mesh to “shrink”:
# Smooth the surface EVEN MORE
smooth = surf.smooth(n_iter=1000)
# extract the edges of the original unsmoothed mesh
orig_edges = surf.extract_feature_edges()
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(smooth, show_edges=True, show_scalar_bar=False)
pl.camera_position = cpos
pl.add_mesh(orig_edges, show_scalar_bar=False, color='k', line_width=2)
pl.show()
Taubin Smoothing#
You can reduce the amount of surface shrinkage by using Taubin smoothing
rather than the default laplacian smoothing implemented in smooth(). In this example, you can see how Taubin
smoothing maintains the volume relative to the original mesh.
Also, note that the number of iterations can be reduced to get the same approximate amount of smoothing. This is because Taubin smoothing is more efficient.
smooth_w_taubin = surf.smooth_taubin(n_iter=50, pass_band=0.05)
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(smooth_w_taubin, show_edges=True, show_scalar_bar=False)
pl.camera_position = cpos
pl.add_mesh(orig_edges, show_scalar_bar=False, color='k', line_width=2)
pl.show()
# output the volumes of the original and smoothed meshes
print(f'Original surface volume: {surf.volume:.1f}')
print(f'Laplacian smoothed volume: {smooth.volume:.1f}')
print(f'Taubin smoothed volume: {smooth_w_taubin.volume:.1f}')
Original surface volume: 597.0
Laplacian smoothed volume: 402.1
Taubin smoothed volume: 589.8
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.253 seconds)